In today’s healthcare landscape, ensuring accurate patient identification and authentication is of paramount importance. patient identification errors can lead to serious consequences, including misdiagnosis, medication errors, and compromised patient safety.
Approaches in current patient identification and authentication
Traditional Methods (Approximately 10%-20%). Despite advancements in technology, many healthcare institutions continue to rely on traditional methods for patient identification and authentication. These include handwritten paper records, identification documents, and patient photographs. However, these methods are susceptible to errors, confusion, and fraudulent activities, leading to uncertainty in patient identity and inaccuracies in information.
Barcode Technology (Approximately 40%-50%). Barcode technology has found substantial adoption in healthcare institutions for patient identification and authentication. Patients are assigned unique barcodes that encode their identity and medical information. These barcodes are scanned to retrieve and verify the data. Although barcode technology offers a certain level of automation and accuracy, it still requires physical contact and manual handling, which can be time-consuming.
RFID Technology (Approximately 30%-40%). RFID technology has gained increasing popularity in the healthcare sector for patient identification and authentication. With RFID, patient identity and relevant information are encoded onto RFID tags. These tags are read and verified using wireless radio frequency signals, eliminating the need for physical contact. RFID technology enables contactless, real-time, and highly automated patient identification and authentication processes. Its benefits include improved accuracy, efficiency, and reduced errors.
By adopting RFID technology, healthcare institutions can enhance patient identification and authentication, leading to improved patient safety, streamlined workflows, and increased operational efficiency. The widespread implementation of RFID technology in the healthcare industry demonstrates its potential and value in ensuring reliable and secure patient identification.
RFID technology offers several unique advantages when it comes to patient identification and authentication
Unlike traditional methods that involve physical contact, such as barcode scanning or manual document verification, RFID operates wirelessly. This contactless approach eliminates the need for direct patient interaction, reducing the risk of contamination and promoting a hygienic environment.
RFID systems enable real-time tracking and identification of patients within healthcare facilities. The technology allows for automatic and instantaneous data capture, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing human error. This enhances efficiency and ensures up-to-date patient information.
RFID systems can easily scale to accommodate a large number of patients and can be integrated into existing healthcare infrastructure. They offer flexibility in terms of tag placement options that can be utilized across various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities.
RFID tags can be programmed to store encrypted patient data, ensuring secure information transmission. Access to patient information can be restricted to authorized personnel, maintaining privacy and confidentiality.
Components
RFID Tags. These tags are attached to patient wristbands and identification cards. Each RFID tag contains a unique identifier and patient data, including their name, medical record number, and relevant medical information.
For instance, DTB’s VW-02 PVC Wristband, specifically designed for patient management, has dimensions of 250*25mm. It utilizes the 13.56MHz chip which supports multiple data writing.
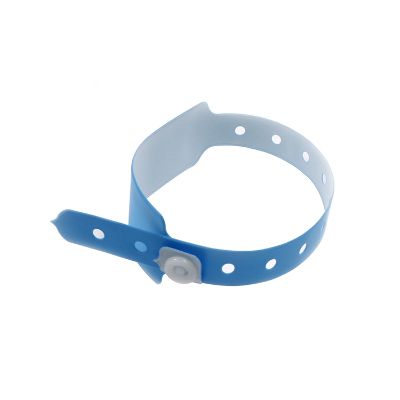

RFID Readers. These devices emit radio frequency signals and are strategically placed throughout the healthcare facility. When a patient comes within range of a reader, the reader captures the signals transmitted by the RFID tag.
Backend System. The captured RFID data is transmitted to a backend system, which processes the information and retrieves the corresponding patient records and authentication data from the hospital’s electronic health records (EHR) or patient management system.
In some cases of successful deployment of RFID systems
Here are three cases of the successful adoption of RFID technology in patient identification and authentication, demonstrating its benefits in enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and patient care.
Stanford Medical Center. Stanford Medical Center, a renowned healthcare institution in the United States, has effectively deployed an RFID system for patient identification and authentication. RFID tags embedded in wristbands are assigned to patients, containing unique identifiers and pertinent medical information. By utilizing RFID readers, medical staff can instantly access patients’ identities and relevant medical records, resulting in enhanced efficiency and accuracy in patient care.
Singapore General Hospital: Singapore General Hospital (SGH), a leading healthcare facility in Singapore, has adopted RFID technology for patient identification and authentication. RFID wristbands are utilized to accurately identify patients, and the system is seamlessly integrated with SGH’s electronic medical records system. This integration facilitates streamlined processes, ensuring precise patient identification and authentication while improving patient safety and care.
The Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital: The Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital (RBWH), located in Australia, has implemented an RFID-based patient identification and authentication system. Upon admission, patients are provided with RFID wristbands that contain unique identification details and relevant medical information. The RFID system is seamlessly integrated with the hospital’s electronic medical records system, enabling real-time access to patient data for precise identification and authentication.
Opportunities and Challenges
As the RFID system is being implemented on a larger scale in healthcare institutions, there are certain challenges and opportunities that need to be considered. While challenges such as infrastructure and cost, staff training and adoption, integration with existing systems, and privacy and security concerns may arise, the benefits obtained are significant, including improved patient safety and streamlined operations through advanced patient identification and authentication systems.
If you have any ideas or considerations regarding the deployment of RFID in healthcare institutions, engaging in a conversation with DTB, the RFID experts, would be a valuable choice. DTB provides a comprehensive range of services, from product offerings to tailored solutions, and can provide insights and expertise to support successful RFID implementation in the healthcare sector.